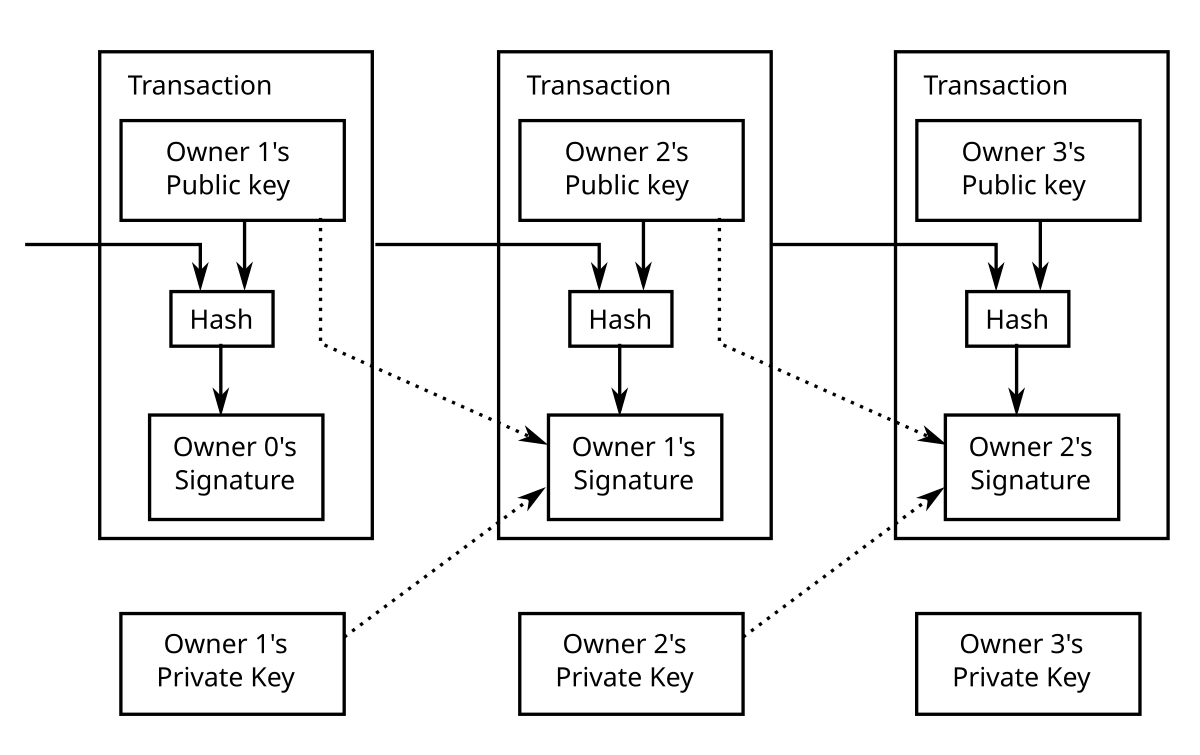
The blockchain's data structure includes two primary components—pointers and a linked list The pointers are the variables, which refer to the location of another variable, and linked list is a list of chained blocks, where each block has data and pointers to the previous block A Merkle tree is a binary tree of hashesEach block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data The three pillars refer to the three most fundamental characteristics of a blockchain structure Blockchain makes the historical scene of any processed resource unalterable and easy forward decentralization and cryptologic hashingOct 09, 14 · Bitcoin blockchain structure A blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked together using cryptography Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data (generally represented as a Merkle tree)
Breaking Down The Blockchain Architecture Artificial Intelligence
Structure blockchain blocks
Structure blockchain blocks-Jun 04, 21 · An algorithm that you can use to calculate the next block in a blockchain C person who just initiates a transaction in the blockchain D person who receives money as the receiver of the transaction This is about Blockchain Structure Thank you@ structure blockchain Share Improve this question Follow asked yesterdayJul 19, 19 · In the blockchain, a block is a core concept that can be thought of as a page in a ledger Blocks contain transactions and some important data such as previous hash that ensures immutability and




Blockchain Nist
A block block in a blockchain is a data structure that stores a set of transaction data in a blockchain Blockchain a blockchain is a decentralized database, or simply a decentralized linked list, where list of records (called blocks) are linked via cryptography Think back to when people Each block in the chain contains a number ofMar 12, 21 · Anatomy of a Block Each Bitcoin block is limited in size to one megabyte of data For "Segregated Witness" (SegWit) blocks, transaction data is limited to one megabyte, whereas signature data (aka witness) is segregated and limited to three megabytes This keeps the block size at one megabyte while increasing block space for transaction dataThere are many types of data structures in the digital world, including blockchain The term blockchain comes from the structure that stores your data All data becomes separated into blocks Every block states which block came before it creating a "chain" of blocks Stating which block came previously is commonly referred to as referencing
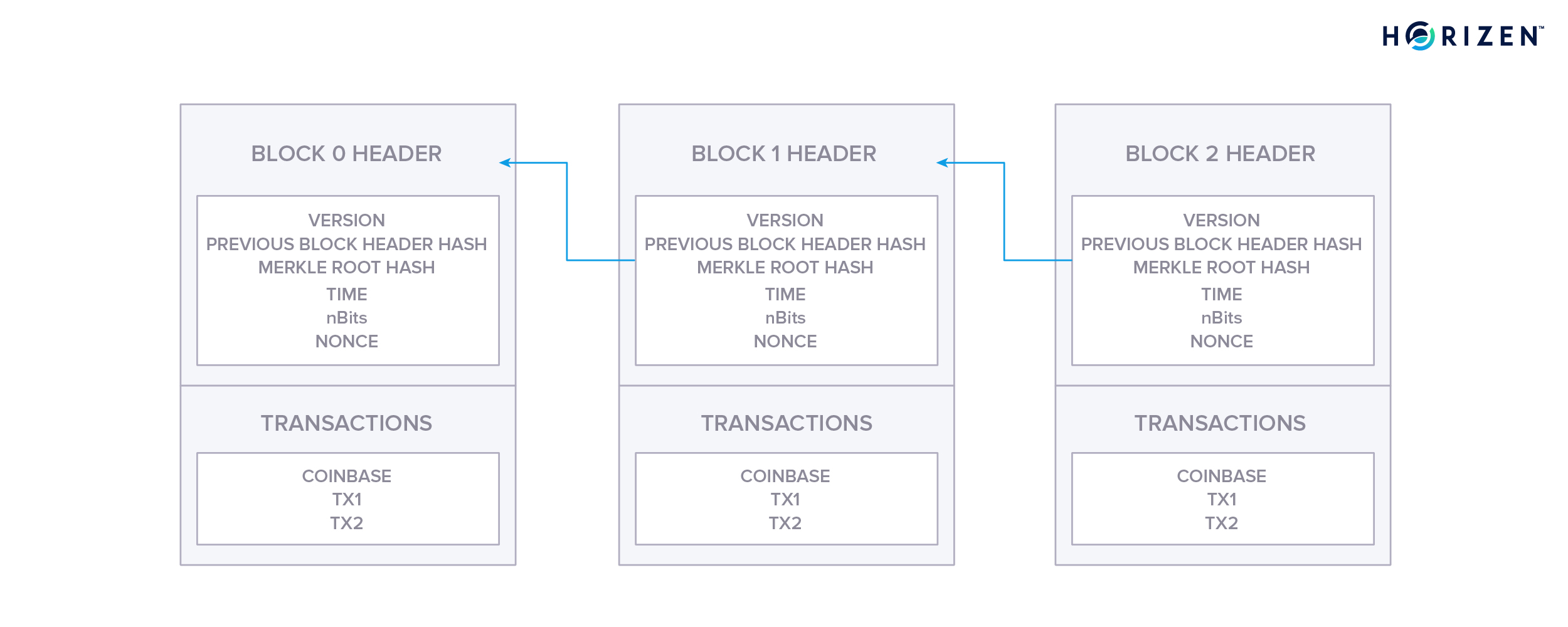
The block in Ethereum is the collection of relevant pieces of information (known as the block header), H, together with information corresponding to the comprised transactions, T, and a set of other block headers U that are known to have a parent equal to the present block's parent's parent No diagram though (an opportunity for the community)Apr 09, 18 · A blockchain,originally block chain, is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked and secured using cryptography Each block typically contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the dataBlockchain The block structureWatch more videos at https//wwwtutorialspointcom/videotutorials/indexhtmLecture By Mr Parth Joshi,
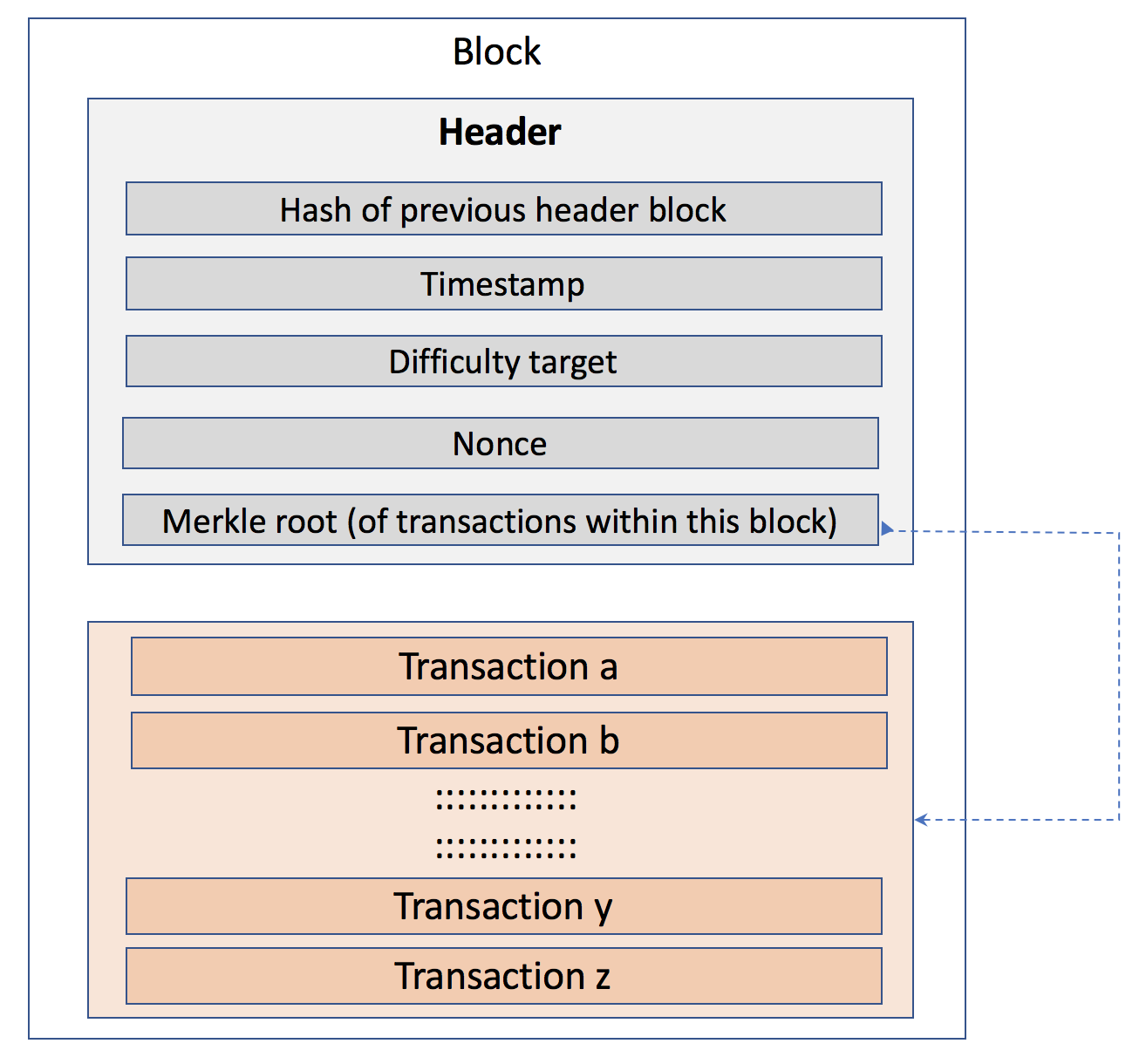
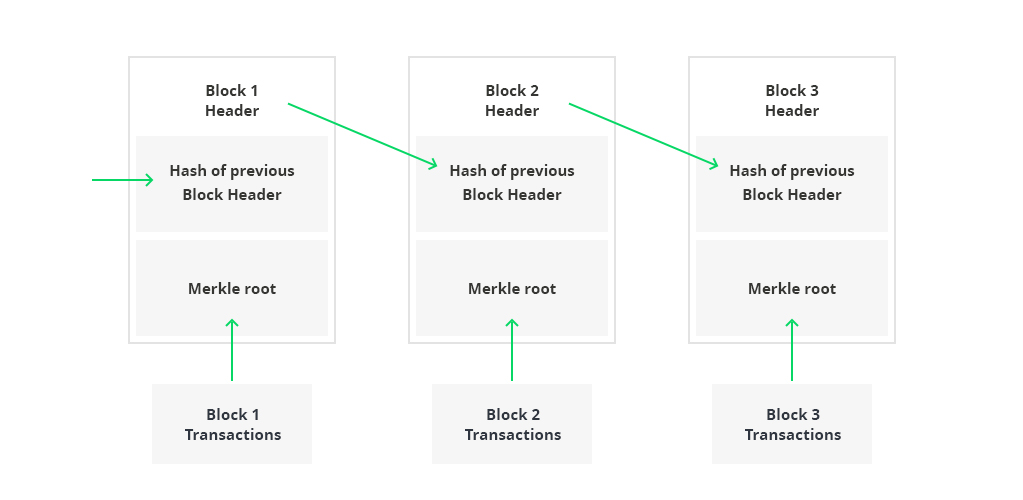
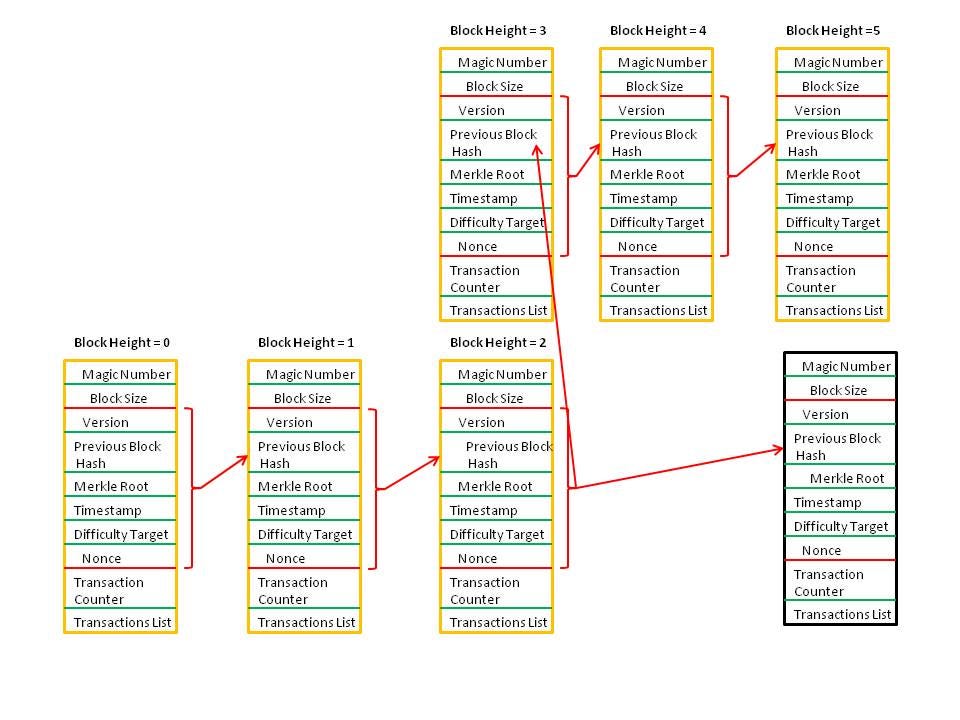
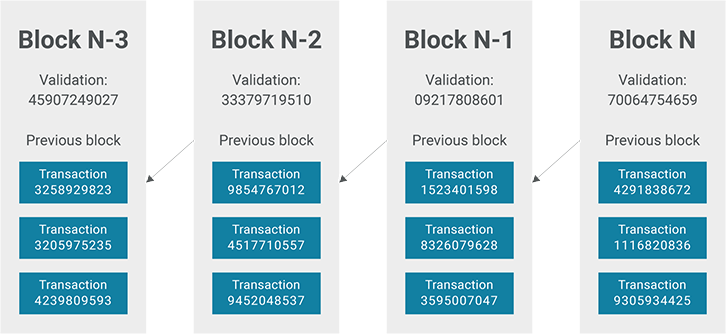
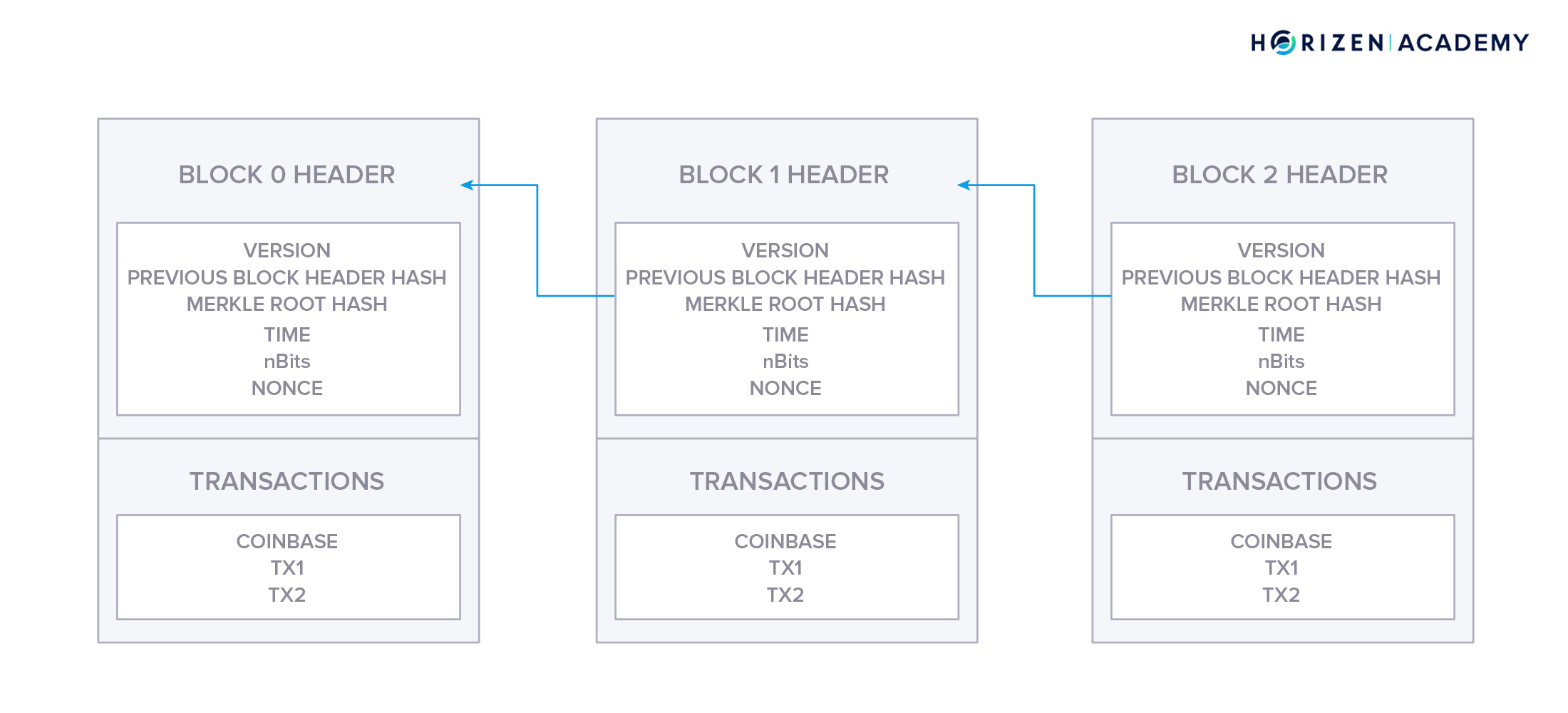
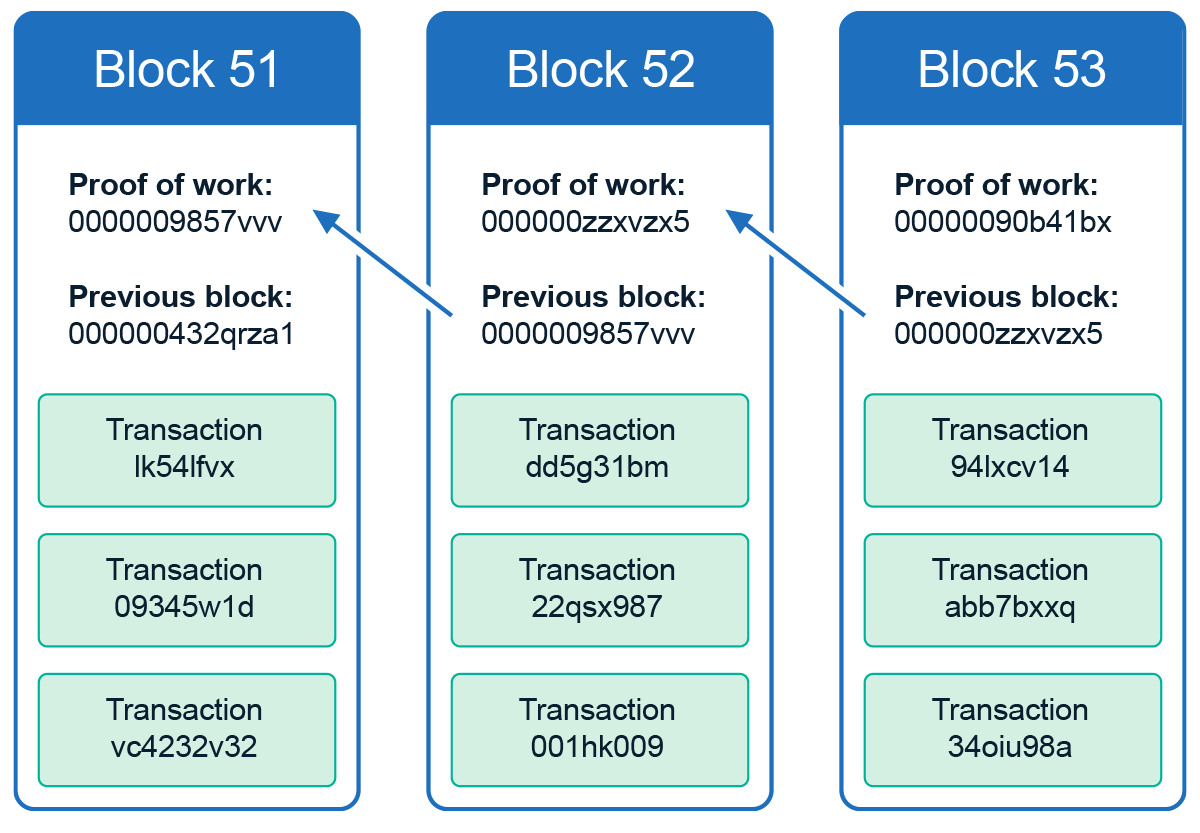
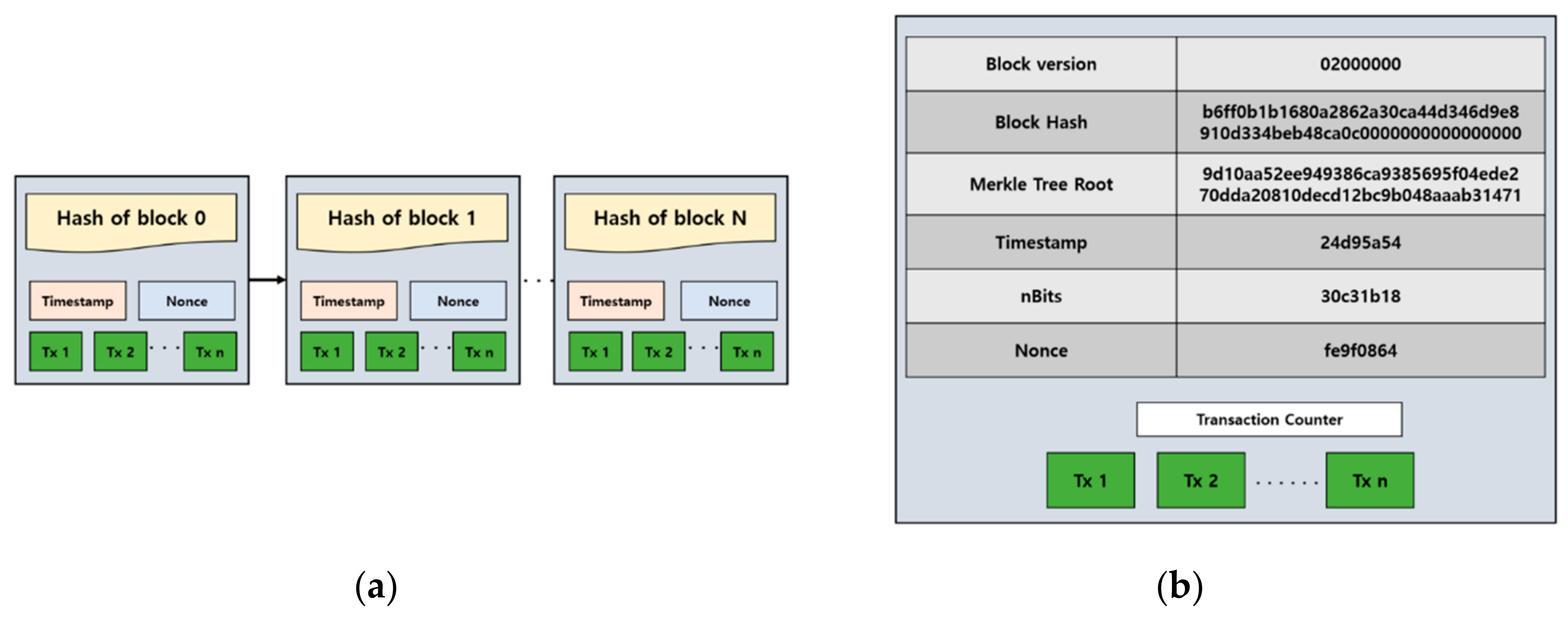
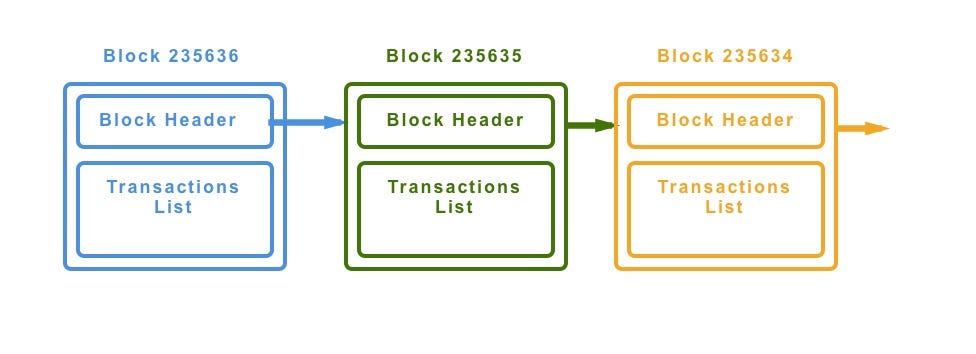
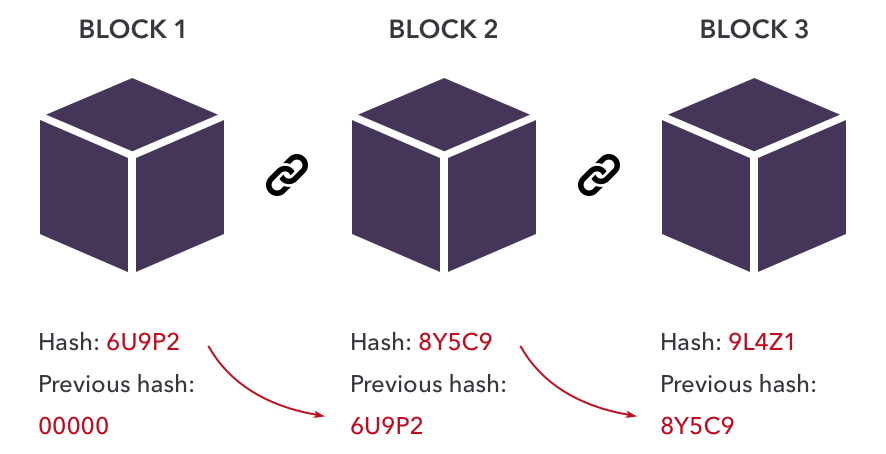
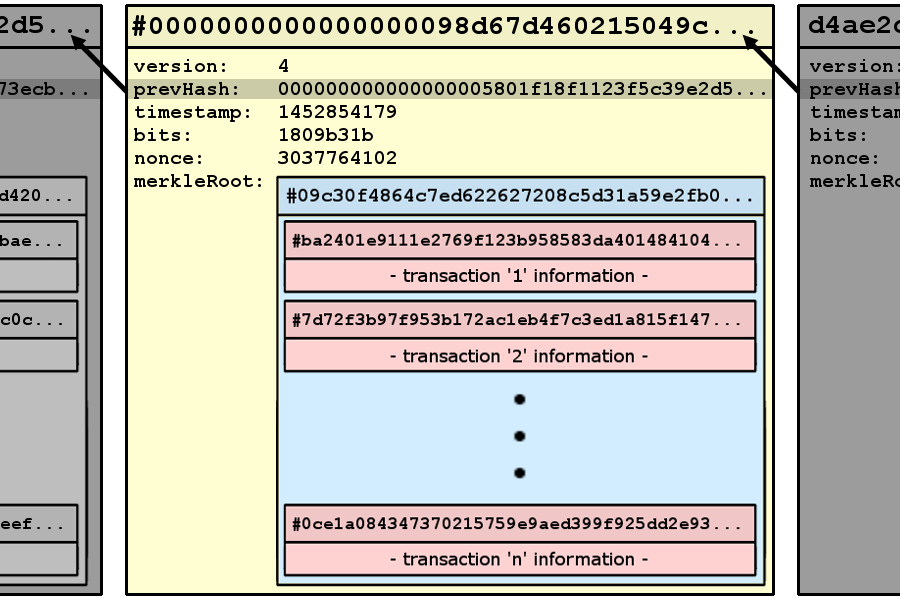
Jan 10, 19 · For the purposes of this article, we will mainly look to Bitcoin's blockchain when discussing aspects of blockchain architecture in general However, the architectural components of transactions, blocks, mining, and consensus can be generalized and implemented in many different ways, leading to various possible blockchain projects These projects usually involveFeb 04, 21 · You also can give each candidate block a block header, which is basically a bunch of metadata about the block Block Header Miners use this metadata when trying to add a block to the blockchain metadata – n data that describes other data, serving as an informative label Block header fields The details of these fields isn't important right now, but here's a quick runthrough anyway Version Describes the structure of the data inside the blockNow, let's look at the structure of the Blockchain by peeking into the Bitcoin Blockchain Our goal is to understand the link between the blocks Let's consider the chain of three blocks 4867, 4868 4869 4868 shown in the middle, has the hash of 4867 as its previous hash




Deploy Your First Ethereum Smart Contract On A Blockchain Theodo



Blockchain Wikipedia
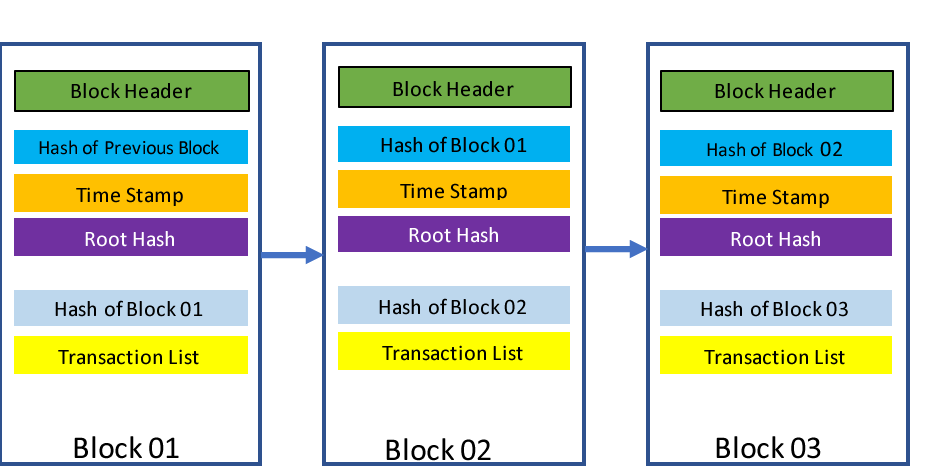
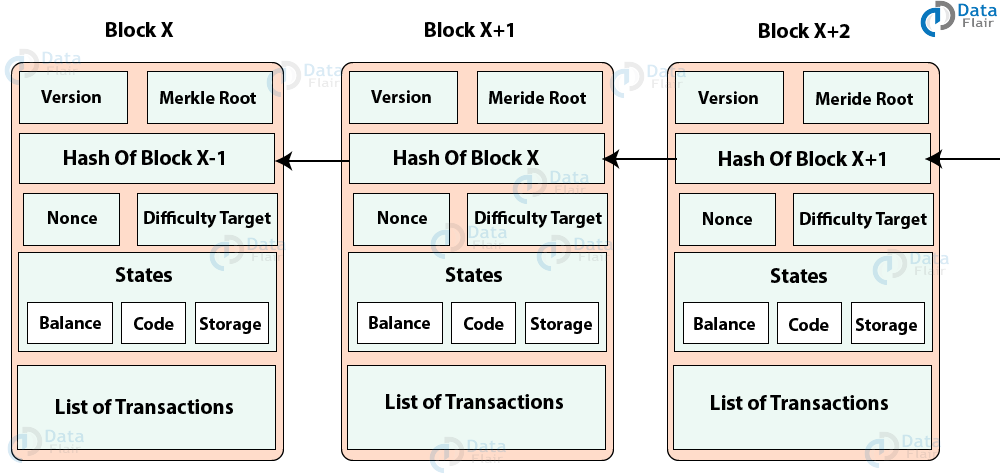
Apr 26, 21 · When discussing the structure of the blockchain, it is often described as a series of blocks that are linked together in a way that protects them against modification However, it is only the headers of the blocks that are actually linked together in this way The header of a block in a blockchain can have a number of different fields, depending on the details of the particular blockchainMar 03, 21 · Blockchain stores data in numerous groups termed blocks Each block has a lot of information, but the space in them is limited So, when the one block is filled with information, it is linked with the previous block creating a chain of blocks, which is why it is known as the blockchainJun 06, 21 · The blockchain data structure is an ordered, backlinked list of blocks of transactions The blockchain can be stored as a flat file, or in a simple database The Bitcoin Core client stores the blockchain metadata using Google's LevelDB database Blocks are linked "back," each referring to the previous block in the chain




Blockchain And Its Structure An Introduction
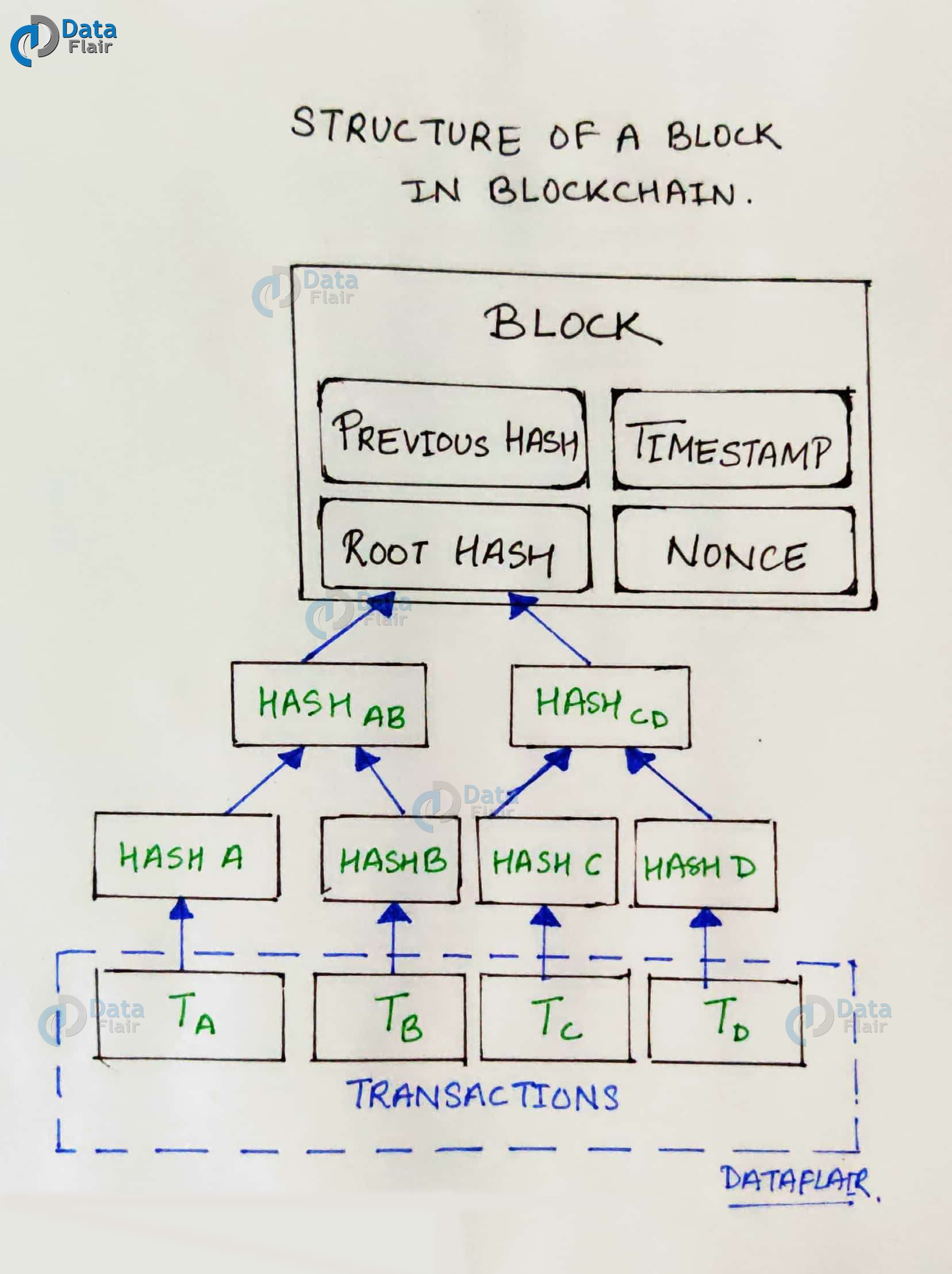



Understanding The Basics Of Blockchain Nourish The Roots Of Technology Dataflair
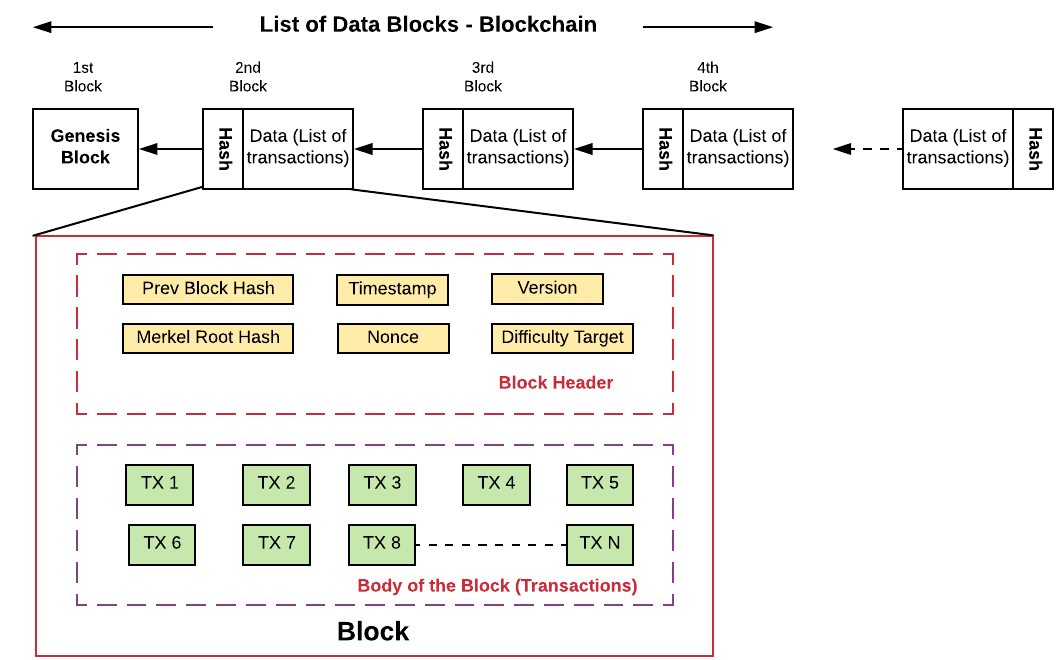
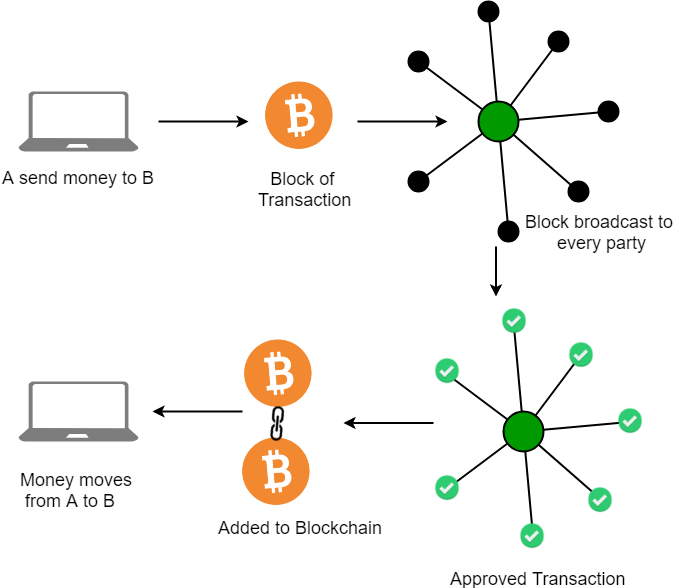
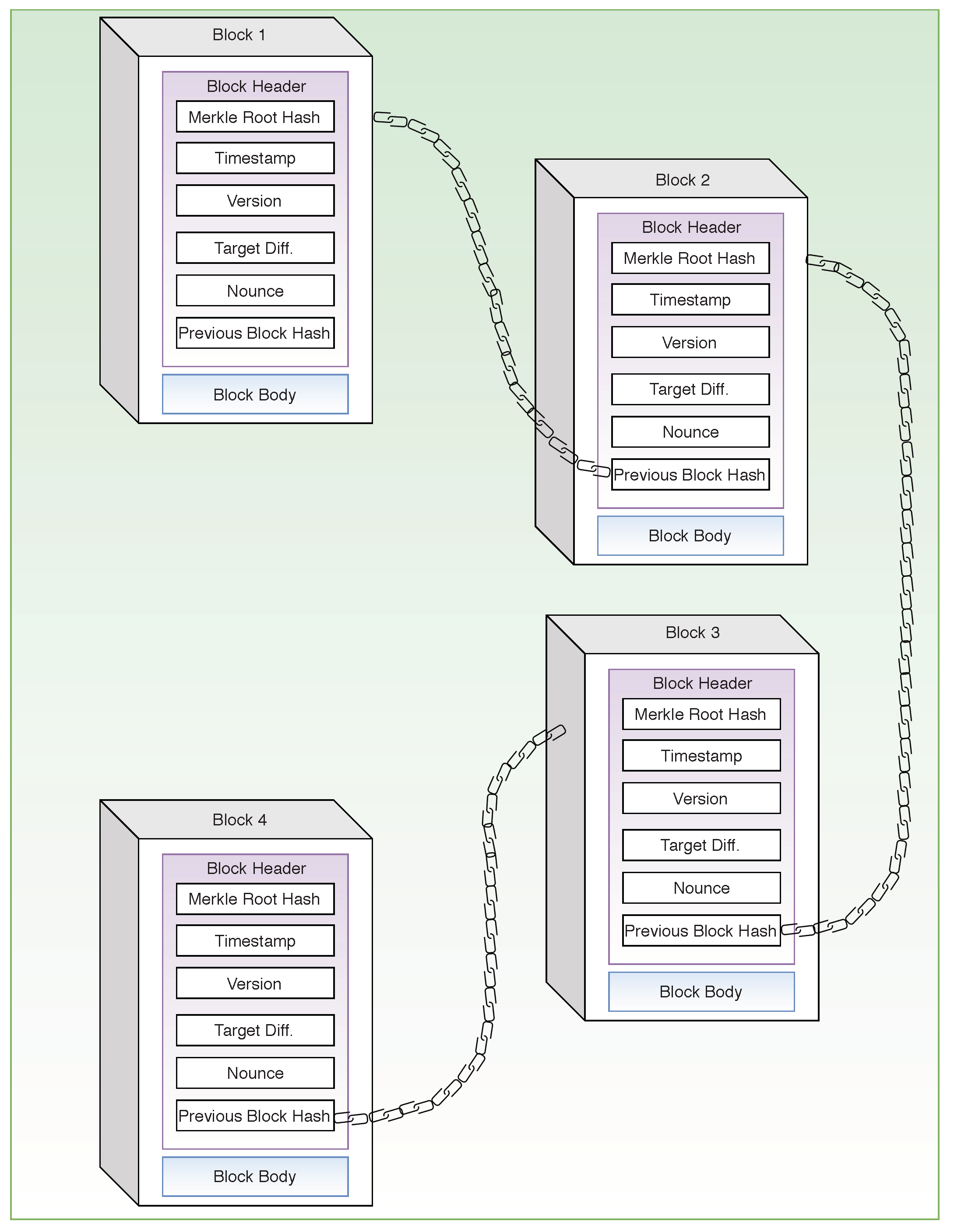
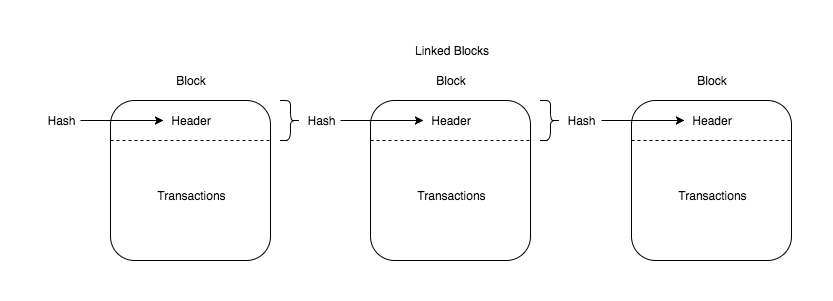
Jun 30, 18 · Blockchain represented as Linked List Data Structure Each block consists of a header section and a body section In case of bitcoin blockchain, a block is of 80 bytes The following is the details The body section of the block may consist of the list of transactions This is as represented in above diagramApr 06, 18 · Blockchain data structure is mainly hash pointer based and involves block as the main data structure Data structures help in the organisation and storage of data in a way that they can be easily accessed and modified Broadly speaking, blockchain data structure can be described as a back linked list of transaction, arranged in blocksMar 31, 21 · 1 Person A logs in to his Blockchain Wallet and initiates a transaction with Person B (Wallets are basically UI which simplifies a user's interaction with the Blockchain 2 Every block
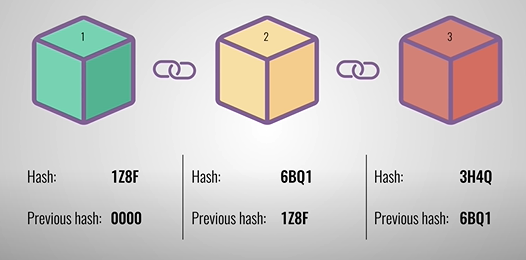



Designing A Blockchain Architecture Types Use Cases And Challenges By Mobindustry Mobindustry Medium
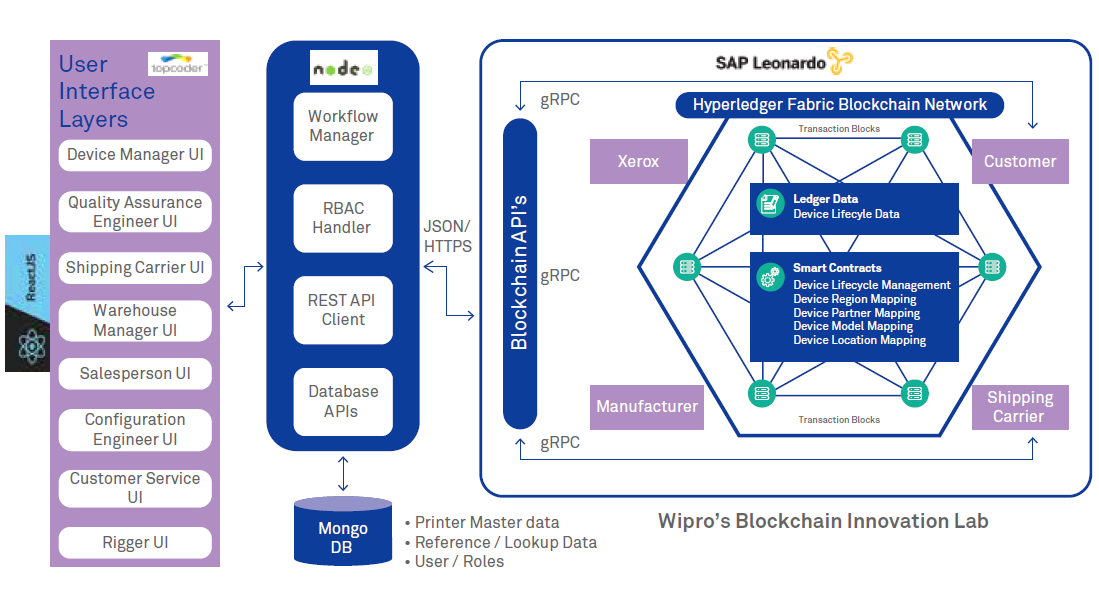



Digital Transformation In Enterprise Architecture How Is Blockchain Useful Wipro
Feb 11, · As the term indicates, Blockchain is a chain of blocks containing a group of transactions or digital data, that are distributed among the millions of users or nodes The transactions may contain information of any kind Since the blocks are chained together, its data can never be changed again, ie the records stored are immutableDec 26, · Ethereum Blockchain For Beginners It's Structure And Operations As we all know that the Bitcoin Blockchain is the mother of all the blockchains It's purpose was to intend peer to peer transfer of value Around 13, some sort of code execution framework was introduced by Ethereum Founders, The centerpiece and thrust of this EthereumJun 07, 21 · Structure of Blockchain network, Blockchain Architecture and Components of Blockchain Search Contribute Add new Article Add new Project Add new Tutorial Add new News News Article Pricing Wishlist Cart You haven't logged In Login Register Help Home Blog JLPCB $2 PCBs Free PCB TURNKEY PCBA PCB Calculator




Blockchain Structure Download Scientific Diagram




8 Reasons Why Blockchain Technology Is The Future Upgrad Blog
Jun 01, 16 · Blocks are therefore organized into a timerelated chain (Fig 6) that gives the name to the whole system blockchain Fig 6 — The block chain sequence structure simplified Transactions in the same block are considered to have happened at the same time, and transactions not yet in a block are considered unconfirmedTo get the blockchain explained even clearer, just imagine a hospital server Blockchain quite literally is a set of blocks containing data, that have been chained together, one on top of another For bitcoin, this means that transactions are permanently recorded and viewable to anyone We've explained the basic structure of a blockchainNow, we are going back to our blockchain directory and next thing we are going to do is make this npm project by doing this Building a blockchain We are going to build a block chain by building a blockchain data structure Creating Block chain Data Structure creating a new block touch blockchainjs testjs cd npm init function Blockchain




Untangling Blockchain A Data Processing View Of Blockchain Systems




How Does Blockchain Work Blockchain Transaction Intellipaat
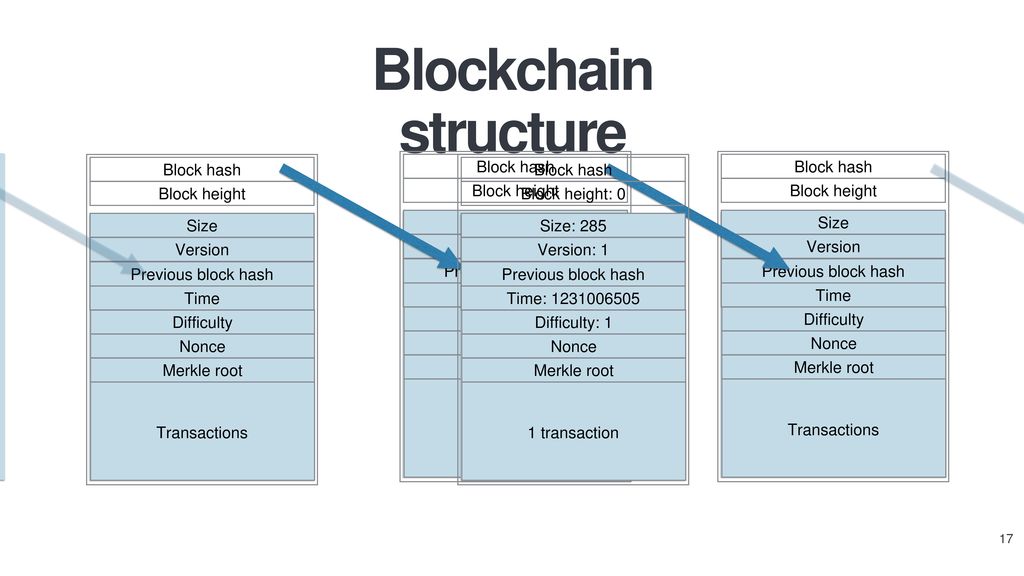
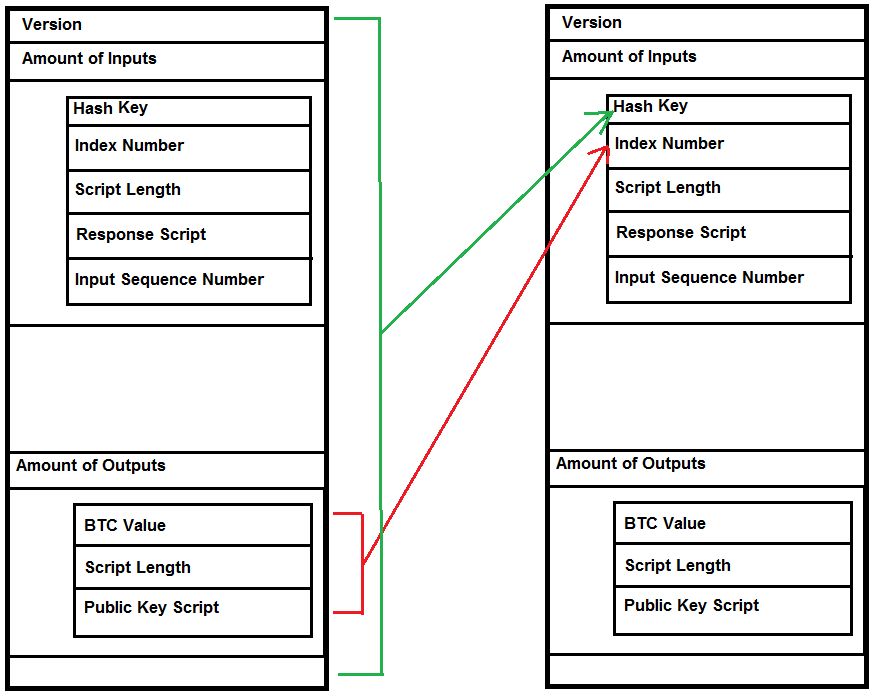
Jun 01, 21 · A blockchain collects information together in groups, also known as blocks, that hold sets of information Blocks have certain storage capacities and, when filled, areSep 09, 16 · The structure of blockchain data is a wellordered, backlinked list of transaction blocks The blockchain can be kept in a simple database, or as a flat file The Bitcoin Core client keeps the blockchain metadata using LevelDB database of Google Blocks are connected "back", each referring to the preceding block in the chainThe Blockchain is a data structure The block is composed of block header and block body As each block has a crpytographic hash of the previous block (refer to PrevHash in the block header), and a chain structure is formed Block Header The data structure of block as following Size Field Name Type Description;



Blockchain Architecture Simplified How It Works Edureka



1
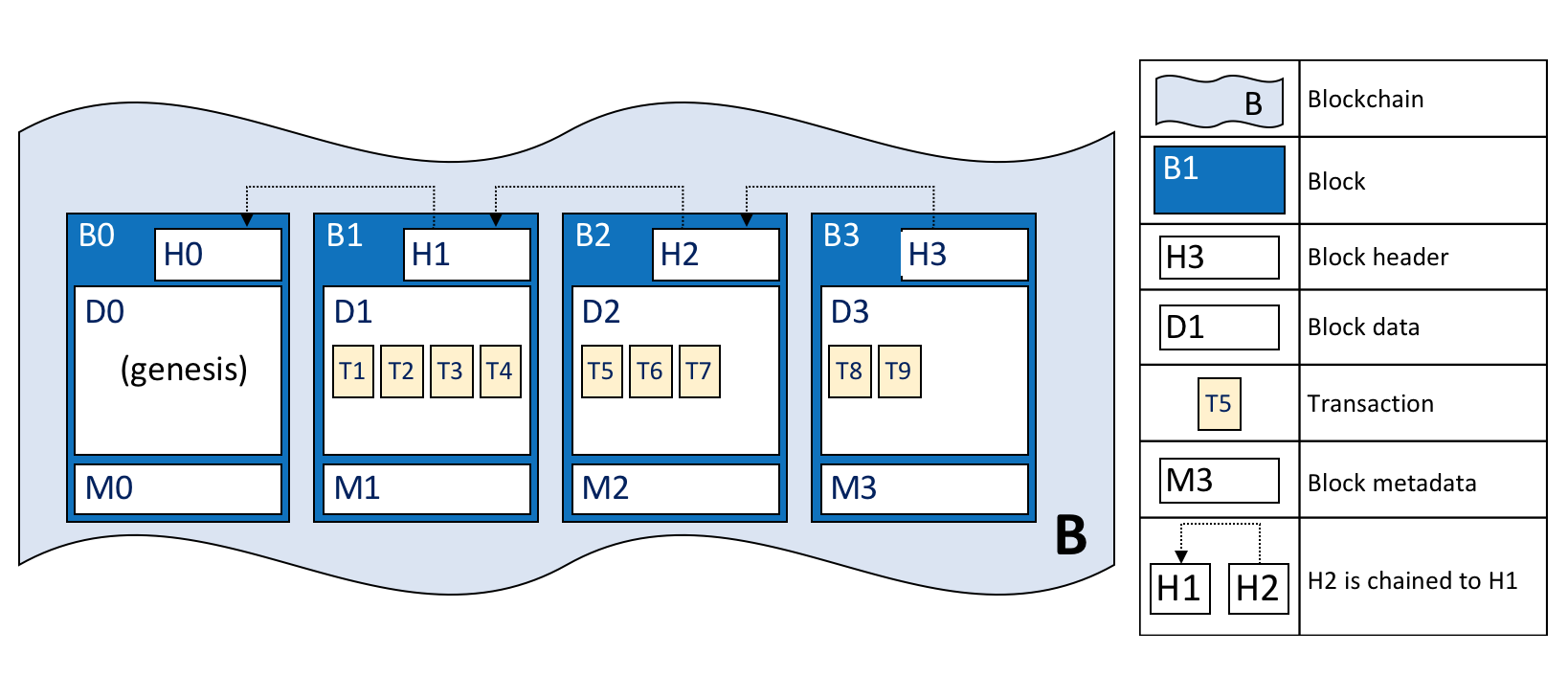
Dec 04, 18 · Data structure of Blockchain The blockchain data structure is a backlinked list of blocks of transactions, which is orderedIt can be stored as a flat file or in a simple database Each block is identifiable by a hash, generated using the SHA 256 cryptographic hash algorithm on the header of the blockA Block block in a blockchain is a Data Structure that stores a set of transaction data in a blockchain A series of Blocks connected together in a linear sequence pattern forms a Blockchain Each data in a block is hashed together with a Nonce number Once a nonce number is generated it means the block is hashed and added to the blockchainBlockchain trilemma is a situation that involves the three basic concepts of blockchain technology Mainly there are three pillars of blockchain technology which helped it gain widespread acclaim transparency The three pillars allude to the three most crucial attributes of a blockchain structure The three pillars of blockchain technology



Is Blockchain A Linked List Like Data Structure Data Analytics
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Blockchain_Sep_2020-02-d8258ab814a34756bf51f1f95c78dc63.jpg)



Blockchain Definition What You Need To Know
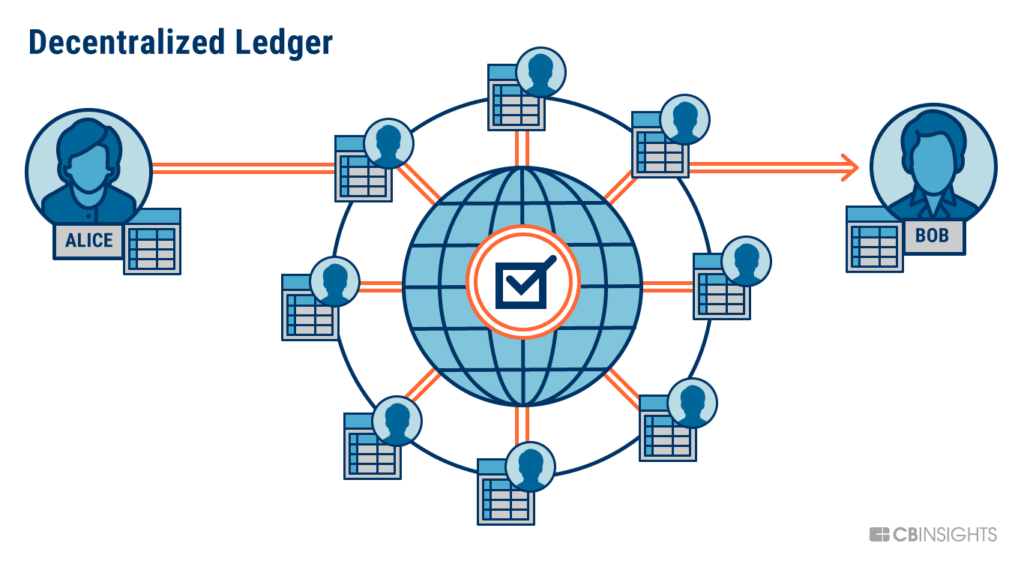
Blockchain is the digital and decentralized ledger that records all transactions According to the wall street journal, a basic blockchain definition states that blockchain is a data structure that creates a digital ledger of all transactions and shares thisMay 21, · The term ' blockchain ' refers to the architecture that comes in the way of storing information in the form of blocks digitally Here 'chain' refers to the database created by the network of computers, correlated within each other Also referred to as Distributed Ledger Technology, a block can be defined as a data structure in itself that needs to qualify theA blockchain is a decentralized, distributed, and oftentimes public, digital ledger consisting of records called blocks that is used to record transactions across many computers so that any involved block cannot be altered retroactively, without the alteration of all subsequent blocks




Features Of Blockchain Geeksforgeeks




Eli5 Blockchain Explained In Simple Terms
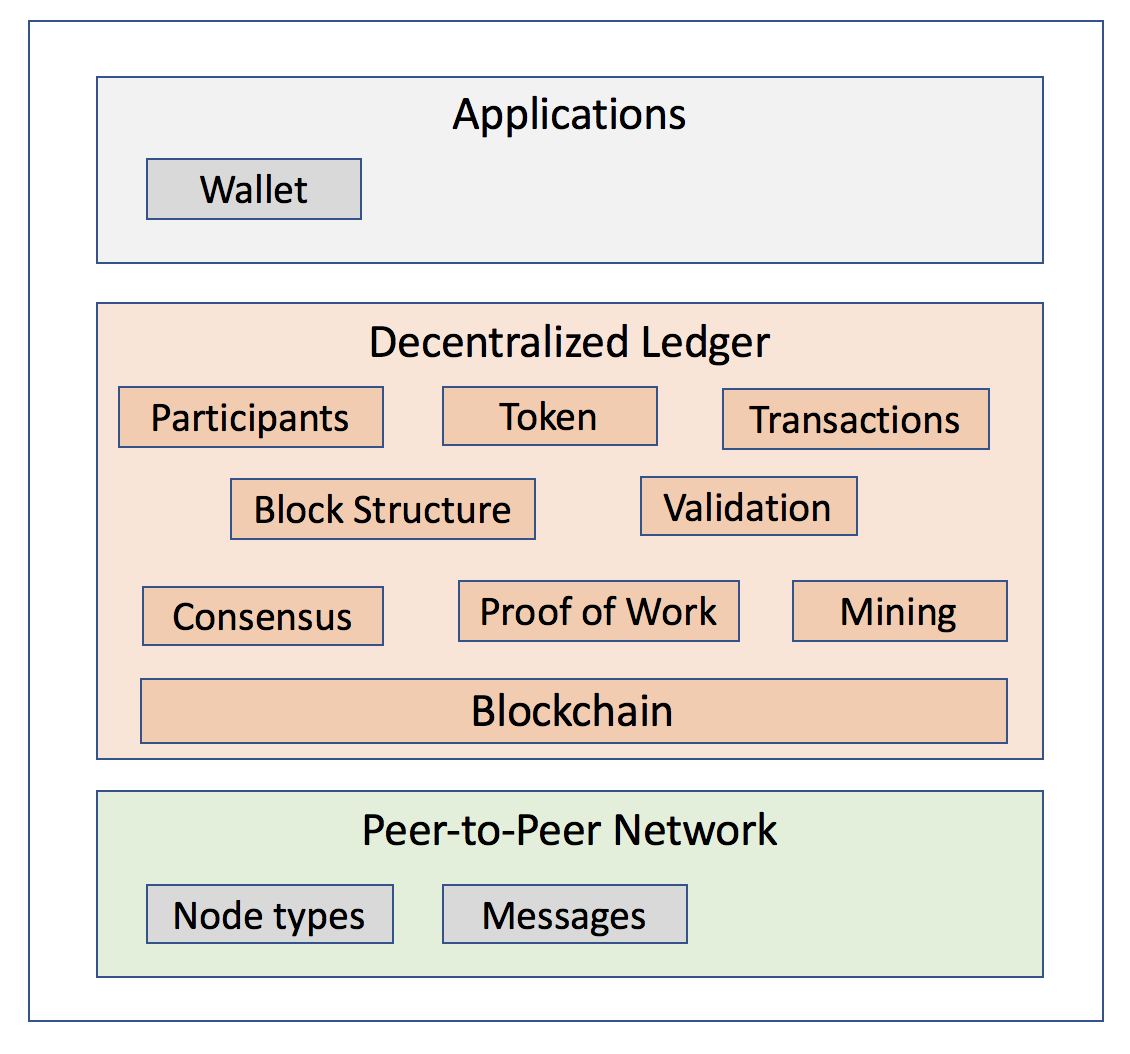
Mar 07, 19 · The structure of blockchain technology is represented by a list of blocks with transactions in a particular order Two vital data structures used in blockchainAug 31, · That's the typically used blockchain structure A chain of block headers, each of which includes the hash of the preceding block and also includes the hash of one data block A matching collection of data blocks, each of which has a hash that is included in one of the blockJan 03, 18 · The blockchain architecture consists of the elements like a node user or computer that has a complete copy of the blockchain ledger, block a data structure used for keeping a set of transactions, and transaction the smallest building block of a blockchain system (records, information, etc) All blocks in a specific order are arranged in




Sap Hana Blockchain Technical Overview Sap Blogs



Blockchain A Technical Overview Ieee Internet Initiative
Jun 07, 21 · The three pillars allude to the three most crucial attributes of a blockchain structure Wondering why blockchain has gained so much popularity in recent years Blockchain technology supports the bitcoin network Let's discuss them in the aspect below Before bitcoin and bittorrent came along, we were more used to centralized servicesAug 31, 18 · The blockchain structure is very similar to that of linked lists or binary trees Linked lists or binary trees are linked to each other using pointers, which point to the previous or next list elements on the nodes in the linked listThe blockchain is a rather sophisticated data structure, made up of many substructures It gives us a set of properties that are paramount to building a decentralized ledger for digital money The Blockchain Blockchain organizes data by splitting it into subsets, referred to as blocks Blocks are similar to the nodes of a linked list




Block Trezor Wiki



Understanding Blockchains And Bitcoin Part 2 Technology Luxsci
Blockchain technologies may be applicable to itsneeds Despite the many variations of blockchain networks and the rapid development of new blockchain related technologies, most blockchain networks use common core concepts Blockchains are a distributed ledger comprised of blocks Each block is comprised of a block



Ledger Hyperledger Fabricdocs Master Documentation



Blockchain Architecture Explained How It Works How To Build



Fit For Purpose Challenges And Opportunities For Applications Of Blockchain Technology In The Future Of Healthcare Bmc Medicine Full Text



Understanding Blockchains And Bitcoin Part 2 Technology Luxsci
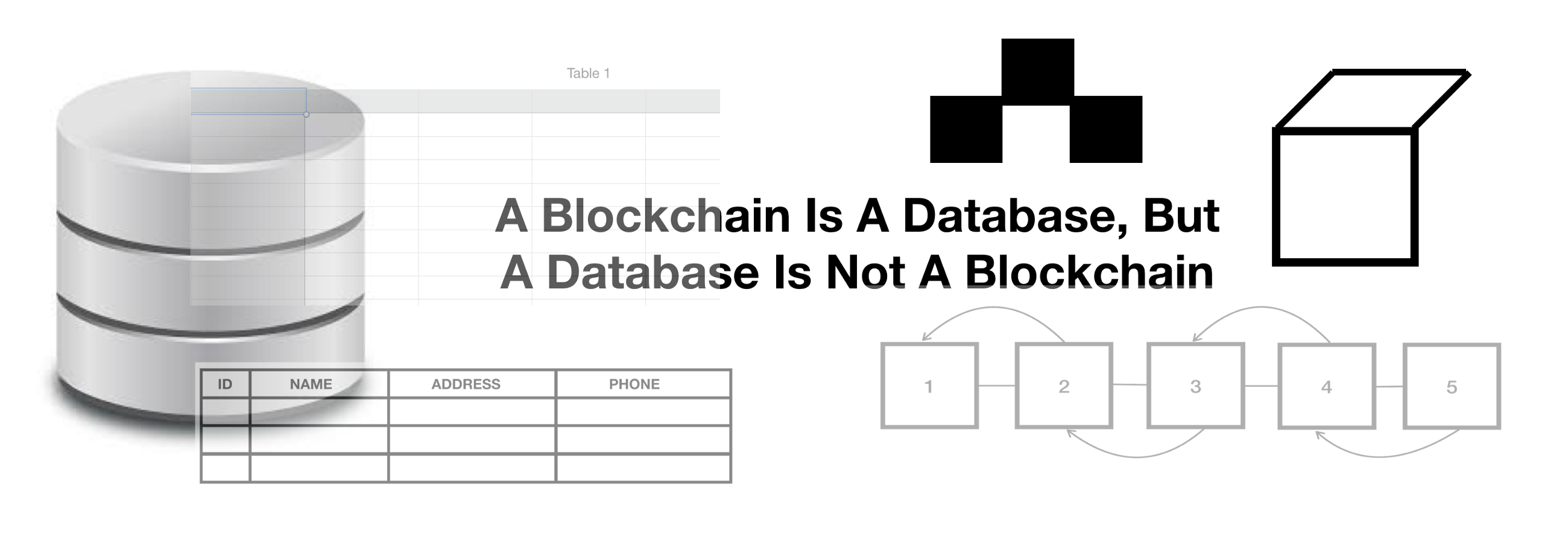



Databases And Blockchains The Difference Is In Their Purpose And Design Hacker Noon




Blockchain A Short And Simple Explanation With Pictures Hacker Noon



Bitcoin S Implementation Of Blockchain By Kiran Vaidya All Things Ledger Medium



Blockchain Technology Ppt Download



Block Chain Bitcoin




Blockchain Data Structure With Block Format Download Scientific Diagram



Introduction To Blockchain Technology Set 1 Geeksforgeeks



Sensors Free Full Text Blockchain In Smart Grids A Review On Different Use Cases Html




Block Structure In Blockchain Download Scientific Diagram
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Blockchain_Sep_2020-01-60f31a638c4944abbcfde92e1a408a30.jpg)



Blockchain Definition What You Need To Know



1




Figure 1 From An Overview Of Blockchain Technology Architecture Consensus And Future Trends Semantic Scholar



A Shallow Dive Into Bitcoin S Blockchain Part 2 Transactions By Andreas Lymbouras Towards Data Science



Bitcoin Internals Part 2 Coding




Blockchain Wikipedia




Blockchain Fundamentals Part 1 Ajith Prabhakar S Weblog




Ethereum Block Architecture Ethereum Stack Exchange




Ethereum Block Architecture Ethereum Stack Exchange



Ledger Hyperledger Fabricdocs Master Documentation




Blockchain Architecture Explained How It Works How To Build




Blockchain Block Structure Download Scientific Diagram




Blockchain Design Structure Showing Chained Blocks With Header And Body Download Scientific Diagram



Blockchain As A Data Structure




Shentilium Technologies




Blockchain And Its Structure An Introduction




How Does Blockchain Work Blockchain Transaction Intellipaat




Polynomial Based Modifiable Blockchain Structure For Removing Fraud Transactions Sciencedirect
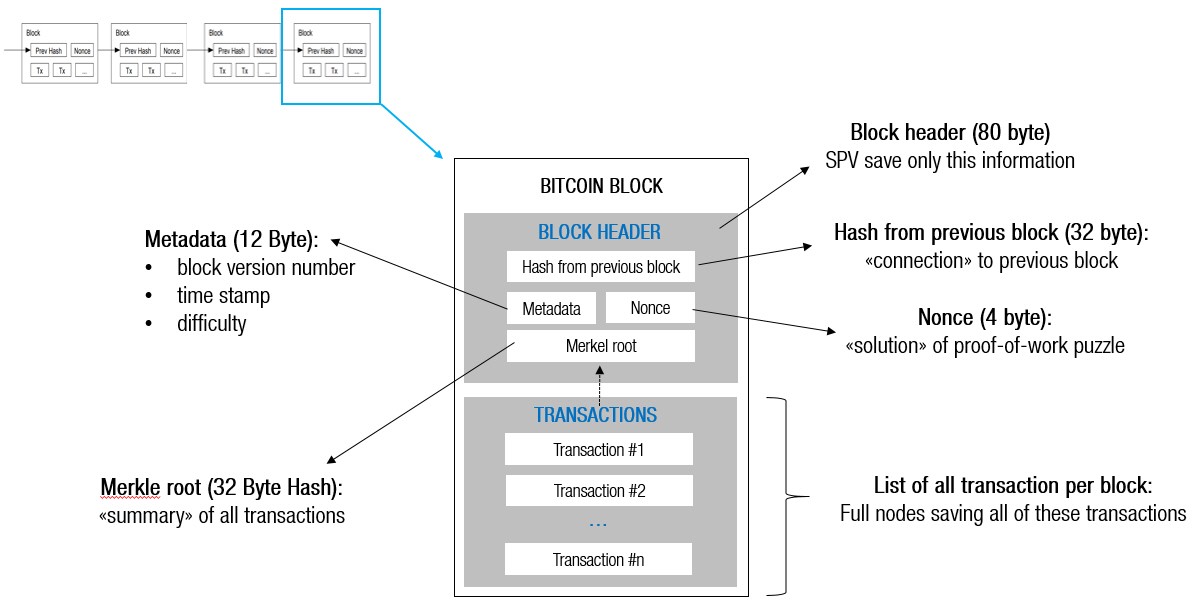



Description Of Bitcoin Blocks And Transactions Marc Steiner




Blockchain Architecture Explained How It Works How To Build



1




What Is A Blockchain Data Structure Primafelicitas




Health Care Blockchain And Innovative Uses Freed Associates



Blockchain As A Data Structure




Blockchain Nist



Blockchain Tutorial Part 1 Fundamentals



Electronics Free Full Text Blockchain Based Secure Storage Management With Edge Computing For Iot Html



1



What Is Blockchain Notes On New Technologies




Architecture Of Blockchain Sciencedirect



Bitcoin Network Wikipedia



Understanding The Basics Of Blockchain Nourish The Roots Of Technology Dataflair



What Is Blockchain Technology Cb Insights Research




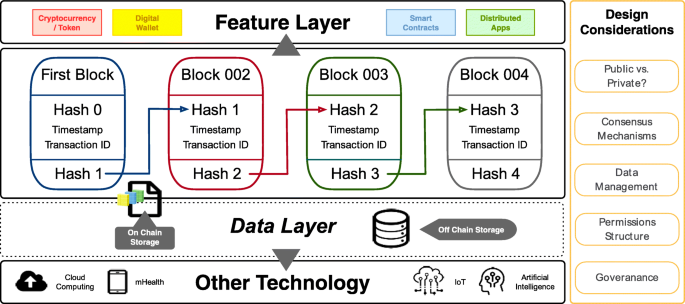
Layered Structure Of The Blockchain Architecture Oracle Blockchain Quick Start Guide



The Bitcoin Blockchain I M Sure You Ve Heard The Word By Sheinix Coinmonks Medium



What Is Blockchain Technology Ig En




Health Care Blockchain And Innovative Uses Freed Associates



Bitcoin Blocks




1 The Structure Of A Blockchain A Block Is Composed Of A Header And A Download Scientific Diagram



Blockchain Architecture The Basics Pluralsight Pluralsight




How Blockchain Could Affect Manufacturing And R D F E Insights




All Bitcoin Mining Should Be Environmentally Friendly Eurekalert Science News




What Is Blockchain Technology A Step By Step Guide For Beginners



Being A Master S Cs Student What Should I Iearn First Blockchain Development Or Data Structure And Algorithm At Top Level Quora




Understanding Blockchain Basic Structure Dev Community




7 The Blockchain Mastering Bitcoin Book




Ethereum Block Architecture Ethereum Stack Exchange



Implementing A Blockchain From Scratch Why How And What We Learned Eurasip Journal On Information Security Full Text



Alexei Zamyatin Taking A Deep Dive Into Merged Mining




Structure Of Blockchain Learn Bitcoin And Blockchain
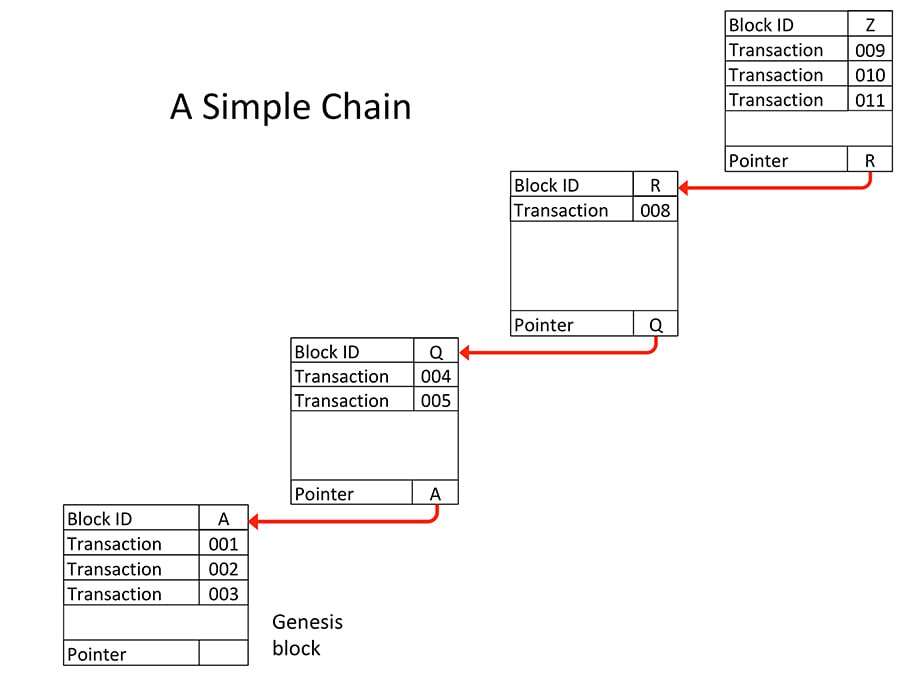



Blockchain The Facts And The Fiction s




Top 5 Use Cases And Platforms Of Blockchain Technology




Blockchain Wikipedia




Blockchain Architecture Explained How It Works How To Build




Blockchain Structure Download Scientific Diagram



Breaking Down The Blockchain Architecture Artificial Intelligence



What Types Of Blocks Exist On The Blockchain Bit2me Academy



Jenny From The Blockchain



1 Minimal Working Blockchain




Blockchain Architecture Explained How It Works How To Build
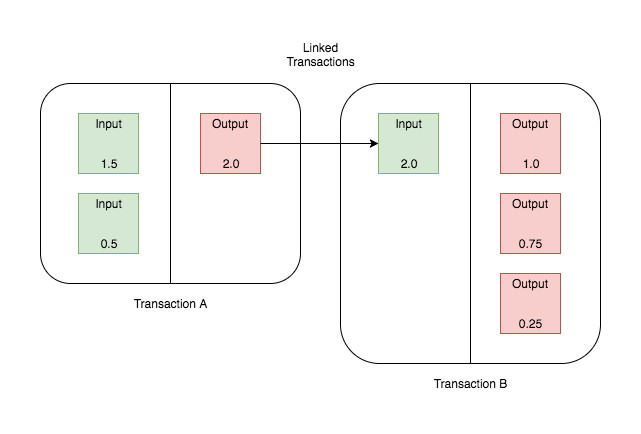



Blockchain Architecture The Basics Pluralsight Pluralsight




Security Of Cryptocurrencies In Blockchain Technology State Of Art Challenges And Future Prospects Sciencedirect
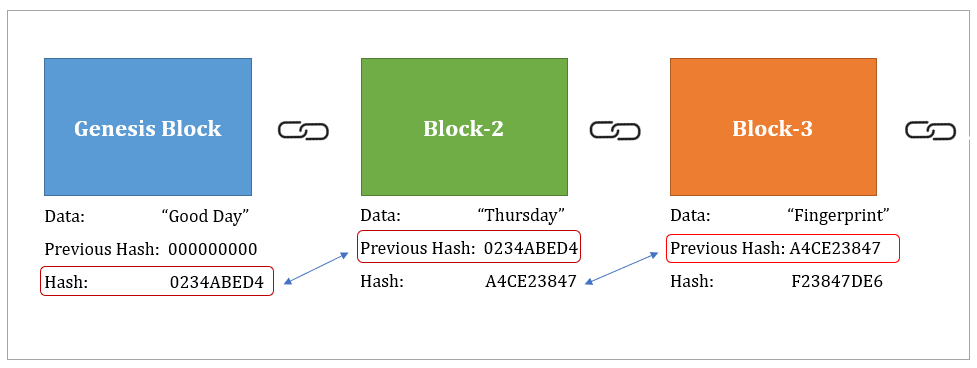



Blockchain Key Characteristics And The Conditions To Use It As A Solution By Venkat Kasthala The Startup Medium




Blockchain Design Structure Showing Chained Blocks With Header And Body Download Scientific Diagram




File Bitcoin Block Structure Svg Wikimedia Commons



How Bitcoin Works Fundamental Blockchain Structure Gemini
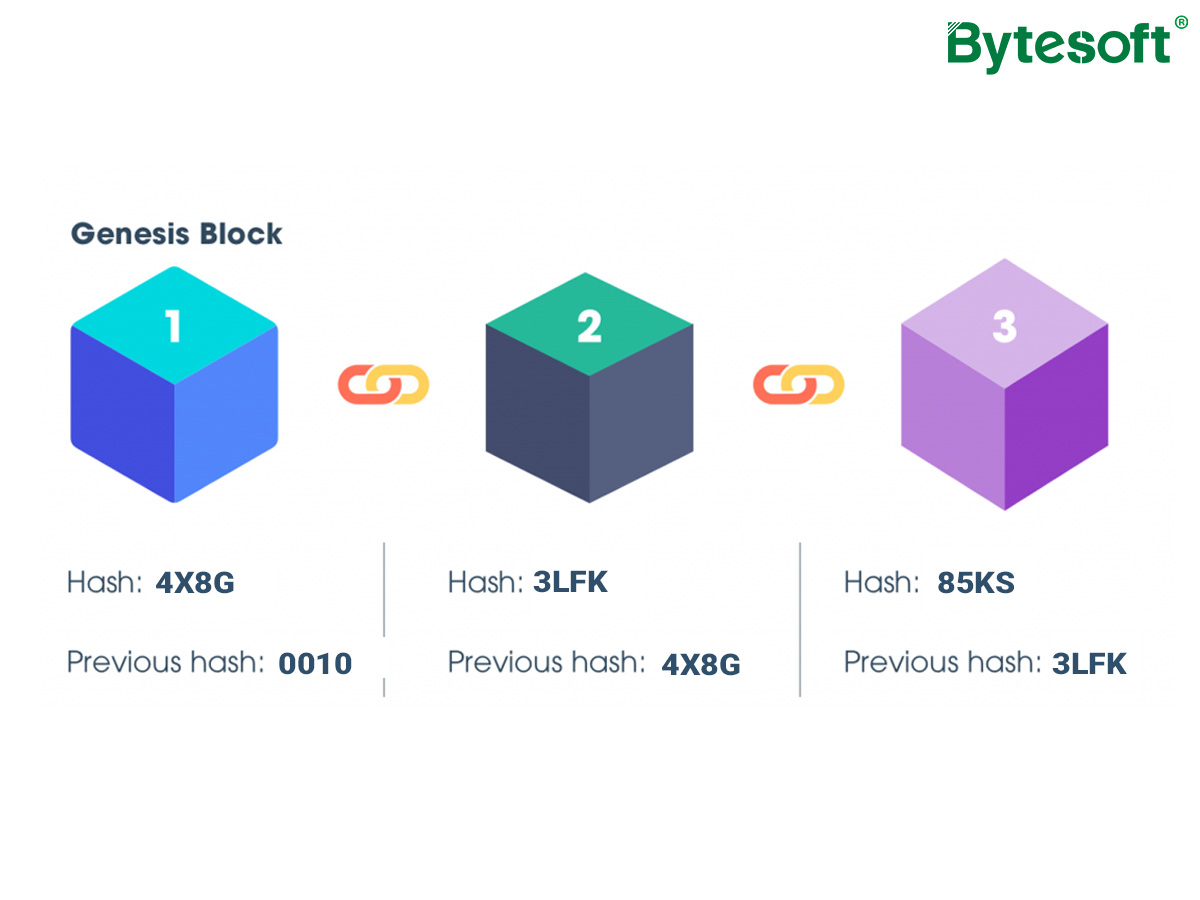



Blockchain Data Structure And How Blockchain Works



Is Blockchain The Answer
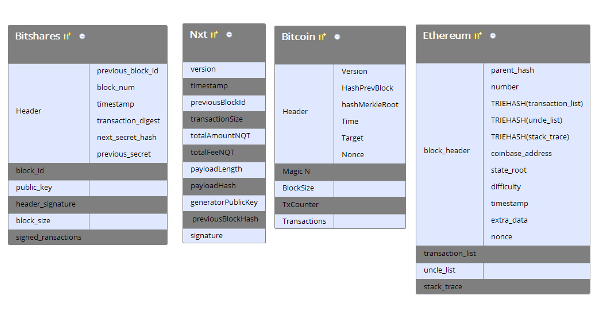



Block Structure In Cryptocurrencies Steemit



The Block Structure Of Bitcoin Blockchain Download Scientific Diagram



Blockchain Technology Basics Spheregen


